User & Group SCIM Synchronisation
Provisioning users and groups to meshStack works based on the SCIM 2.0 standard.
We provide an SCIM API that enables external systems such as Microsoft Entra ID to directly
manage up-to-date user and group information within meshStack. Provisioning means changes about users and groups
in the external system are automatically mirrored to the provisioned equivalents in meshStack. For example, when
the members of a certain Entra ID group are changing and provisioning is set up, those changes will be reflected in the group within meshStack as well
without additional effort. That way we can model the complete lifecycle of users and groups automatically.
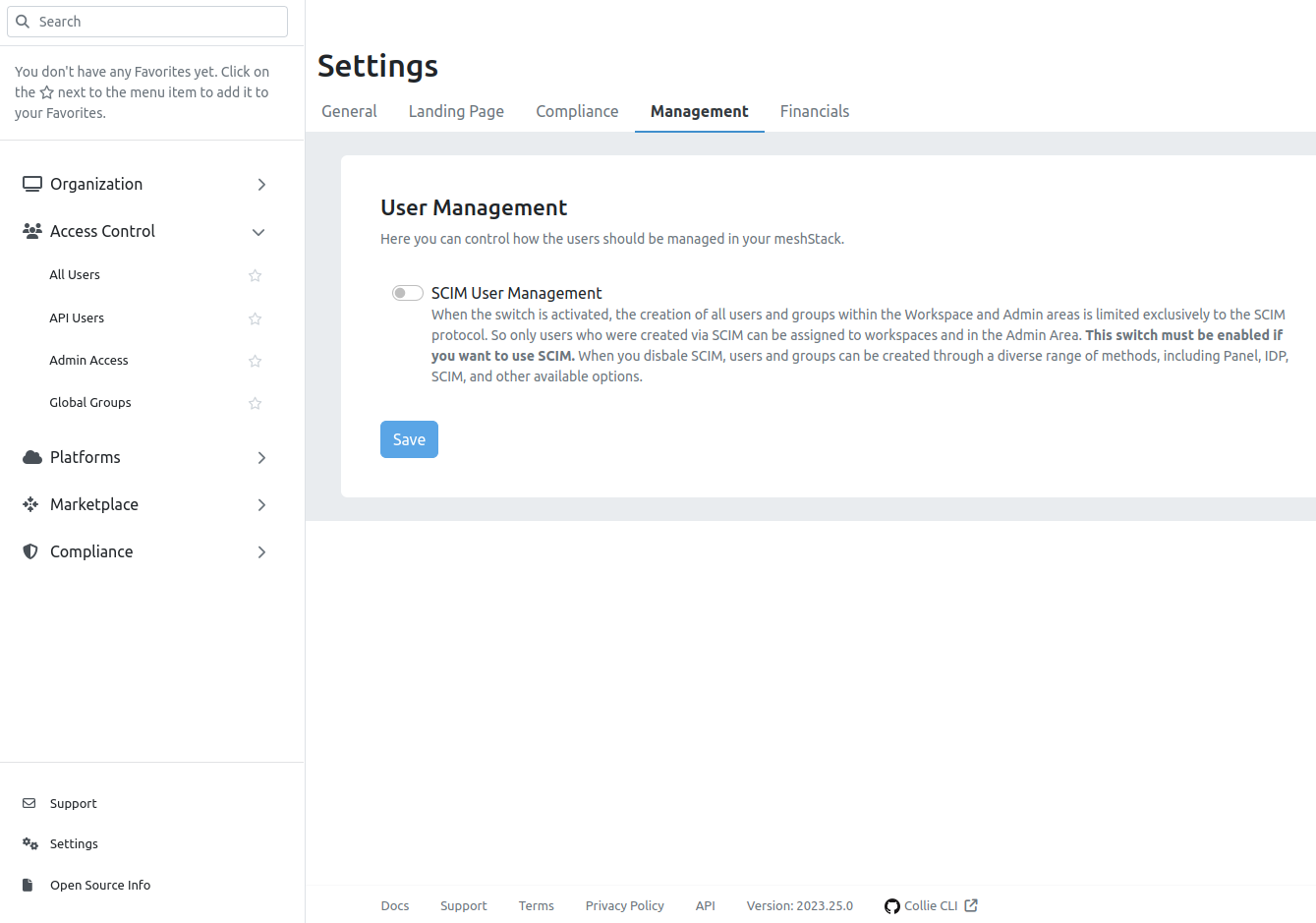
Enable SCIM
By default, in meshStack, users can be created using a variety of methods such as the Panel, IDP, and other available options. If you prefer to manage your users exclusively via SCIM, you need to enable this setting in the Admin area. This disables all other methods to prevent conflicts and double assignments. To enable SCIM, go to the Settings page in the Admin area, and in the 'Manage' tab, turn on the 'SCIM only user management' button. By default, this button is turned off, allowing users and groups to be created through other means.
Provisioning with SCIM
SCIM clients are the source for users and groups. They need to address users and groups in order to manage the creation,
updates and deletion. Because they cannot know user or group identifiers in advance they will attempt to find a user or
group by a unique attribute: for users it selects the userName, for groups it uses the displayName. As a result these fields need to be unique.
To support a wider range of userName formats, meshStack will look up users by their username and uses the email
as a fallback.
Attention Each SCIM client handles requests a bit differently. The way the scope of the synchronization is specified plays a huge role when it comes to load and performance. Because of this we specify the officially supported amount of groups and users for each client for now. For the AAD SCIM client we support the synchronization of an unlimited amount of groups with a maximum of 250 users each at the moment. If you want to sync more users please reach out to us via support@meshcloud.io.
Example
The Entra ID as an SCIM client looks up an existing user by calling:
GET .../api/scim/v2/Users?filter=userName+eq+"johndoe@company.com"
Let's assume there is a user with the username johndoe@company.com, then meshStack will then answer with an SCIM ListResponse containing
the matching UserResource, e.g. like this:
{
...
"Resources": [
{
"schemas": [
"urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:core:2.0:User"
],
"id": "54fbbbaa-c80c-49df-b13d-27133cb81740",
"userName": "johndoe@company.com",
...
}
],
...
}
From that response the Entra ID retrieves the user's id and can from now on refer to this user with the identifier 54fbbbaa-c80c-49df-b13d-27133cb81740.
Let's further assume that the Entra ID wants to update the members of a group with the identifier d90c1657-63b1-44be-8cdc-e3a8ffc5a7d1 and the aforementioned user
is the only member, then the Entra ID will send the following PatchOperation:
PATCH .../api/scim/v2/Groups/d90c1657-63b1-44be-8cdc-e3a8ffc5a7d1
{
"schemas": [
"urn:ietf:params:scim:api:messages:2.0:PatchOp"
],
"Operations": [
{
"op": "Add",
"path": "members",
"value": [
{
"value": "54fbbbaa-c80c-49df-b13d-27133cb81740"
}
]
}
]
}
SCIM API limitations
The SCIM standard introduces comprehensive functionality to work with user and group resources. The implementation of meshStack's SCIM API does not support all features of SCIM. Here is a list of current limitations:
- SCIM endpoints on
/ResourceTypesand/Schemasare not supported - Filtering options to search resources are reduced:
- For users: only simple equals filters on one of the following fields:
id,userName,externalId - For groups: only simple equals filters on one of the following fields:
id,displayName
- For users: only simple equals filters on one of the following fields:
- The parameter for excluded attributes in the search endpoints is limited:
- For users to:
name,userName,emails - For groups to:
members,displayName
- For users to:
Global Groups
The established concept of a group in meshStack is called a "meshWorkspaceUserGroup". Those are always related to a meshWorkspace, so they exist with a relation to one. With the provisioning of users and groups to meshStack we introduce a new type of groups called "global groups". Those are not owned by a meshWorkspace but are rather available to all of them. They cannot be modified manually or programmatically but are synced only via an external system, in this case an Azure AD. Assignment of global groups to meshWorkspaces and meshProjects within the meshPanel works the same way as it does for meshWorkspaceUserGroups.
AAD Configuration
The following guide shows how Microsoft Entra ID can be configured to enable SCIM user and group provisioning to meshStack. In order to connect to meshStack you will need a Basic Authentication user with permissions to access the SCIM Api. Please refer to the Authentication section within the API Docs for the credentials configuration.
General Setup Steps
To set up the provisioning on Entra ID side, have a look at Microsoft's guideline and please follow these steps:
-
Enable SCIM in meshStack.
-
Create a new non-gallery Enterprise Application (EA) in your Entra ID that is dedicated to the provisioning. A step-by-step guide is available here.
-
In the EA set up the meshStack endpoint as target API:
- Go to the "Provisioning" section and then to "Admin Credentials"-
- Use your meshStack's backend URL as endpoint:
https://api.<meshStack>/api/scim/v2/(in older meshStacks you may need to usemeshfedorfederationinstead ofapiin the URL). - Create an API user with permission
Use all SCIM endpoints provided by meshStackin meshStack.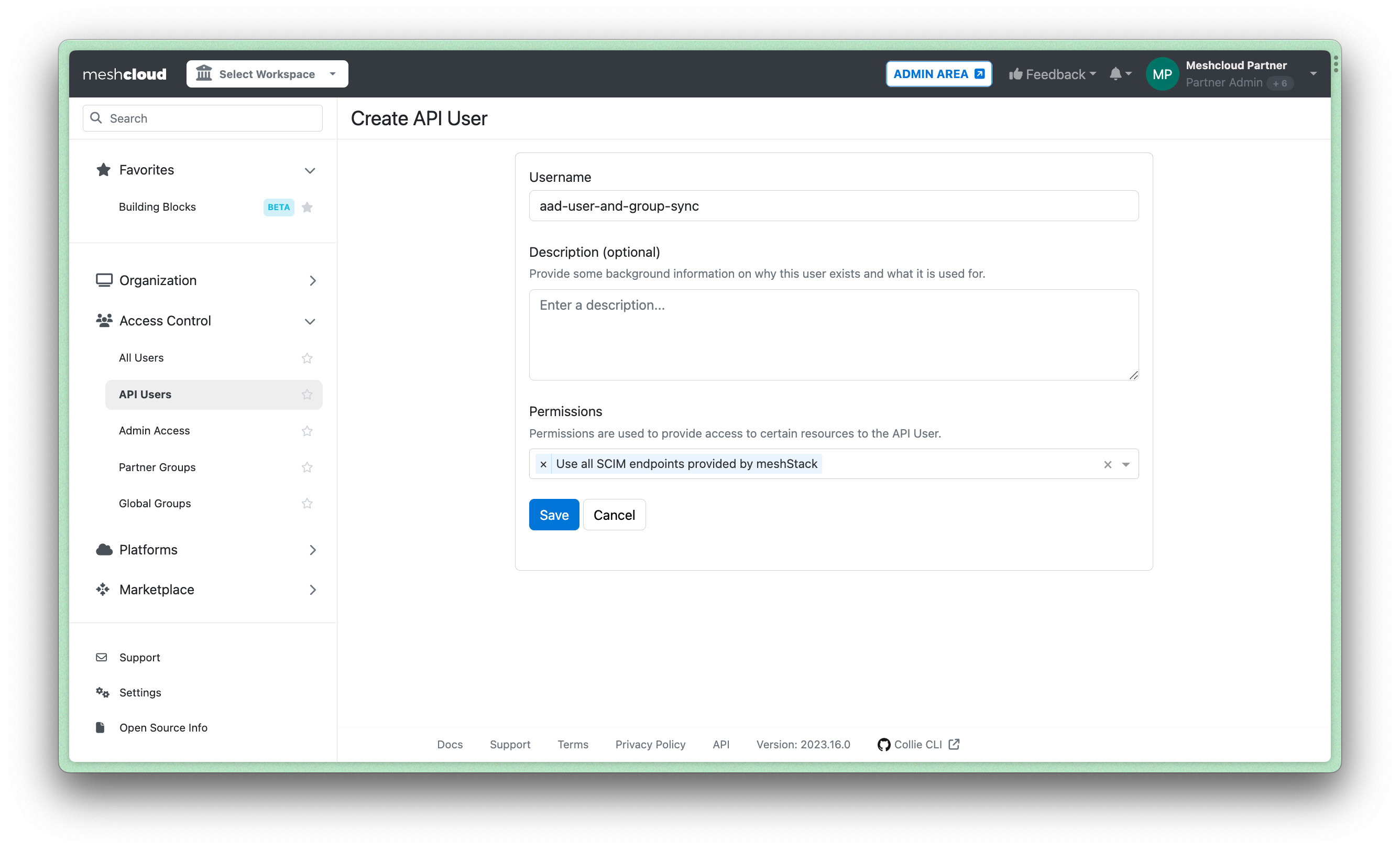
- Set the base64 encoded Basic Auth Credentials as "Secret Token".
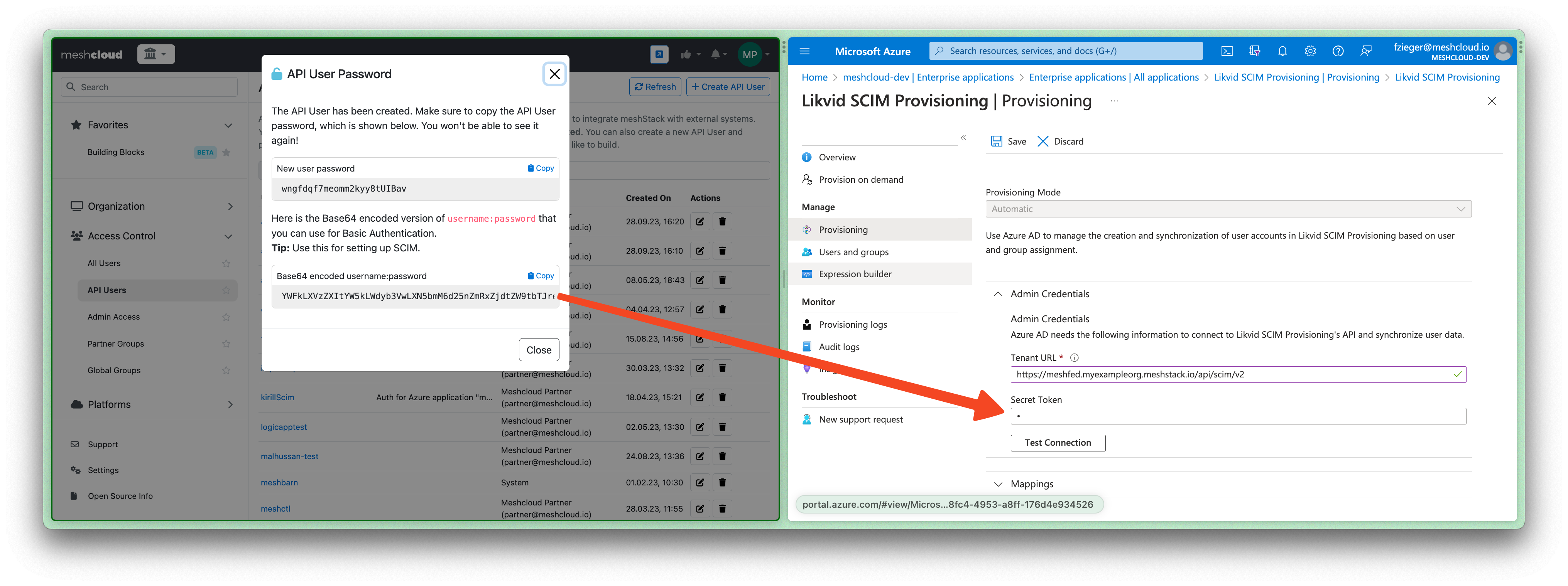
-
Go to "Settings" menu within "Provisioning" and configure which users and groups should be provisioned. You can either:
- Sync only users and groups that are assigned to your EA.
- Sync all users and groups from your Entra ID. This option should always be combined with Scopes as described in the step below.
-
To fine-tune which users and groups are synced go to "Provisioning", then "Mappings" and then to "Users" / "Groups". For users and groups you can separately define Scoping Filters as described in the official guidelines from Microsoft.
- Add filter rules by navigating to the
Attribute Mapping, then go toSource Object Scopeand selectAdd scoping filter. This applies for both groups and users.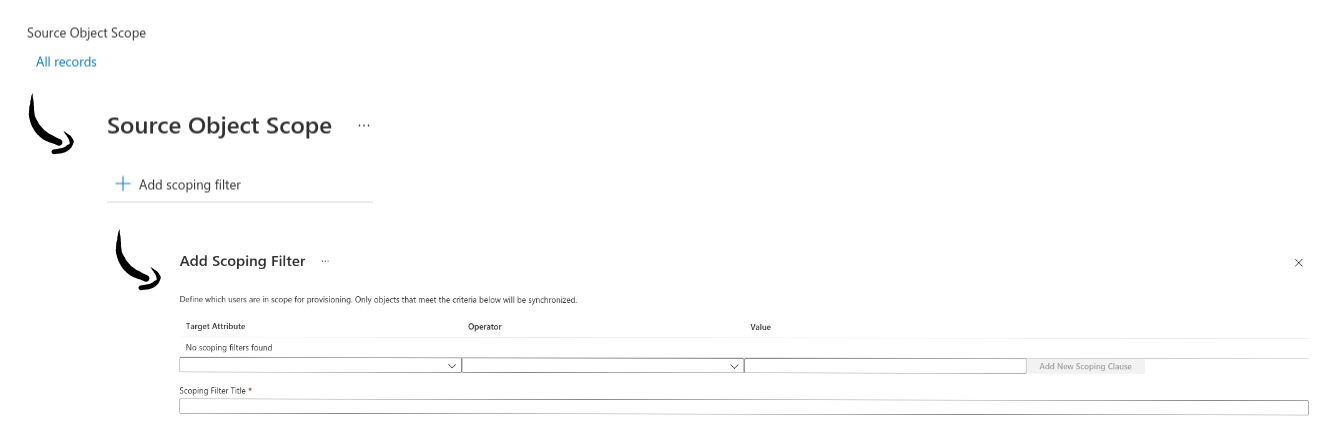
- Add filter rules by navigating to the
-
In the Mapping for Users make sure that you have the mappings configured as described in the user mappings table and remove all other mappings. Note that the externalId attribute should be mapped to the AAD Attribute that is used as the euid in meshStack.
-
Start the provisioning process and regularly monitor the provisioning logs.
User Mappings Table
| AAD Attribute | SCIM app attribute (meshStack) |
|---|---|
| userPrincipalName | userName |
| Switch([IsSoftDeleted], , "False", "True", "True", "False") | active |
| displayName | displayName |
| emails[type eq "work"].value | |
| givenName | name.givenName |
| surname | name.familyName |
| Join(" ", [givenName], [surname]) | name.formatted |
| Attribute which is used as euid in your meshStack | externalId |
How to map attributes via expressions
In various scenarios, modifying user attributes before synchronizing them with meshStack can be beneficial. For instance, certain organizations require the utilization of specialized user accounts for administrative tasks. These "admin users," in contrast to "normal users" employed for daily office activities, frequently lack email attributes. The following is a method to establish a mapping that assigns the email attribute using an expression.
Navigate to the enterprise application and open the expression builder. Use the expression builder to build the desired expression.
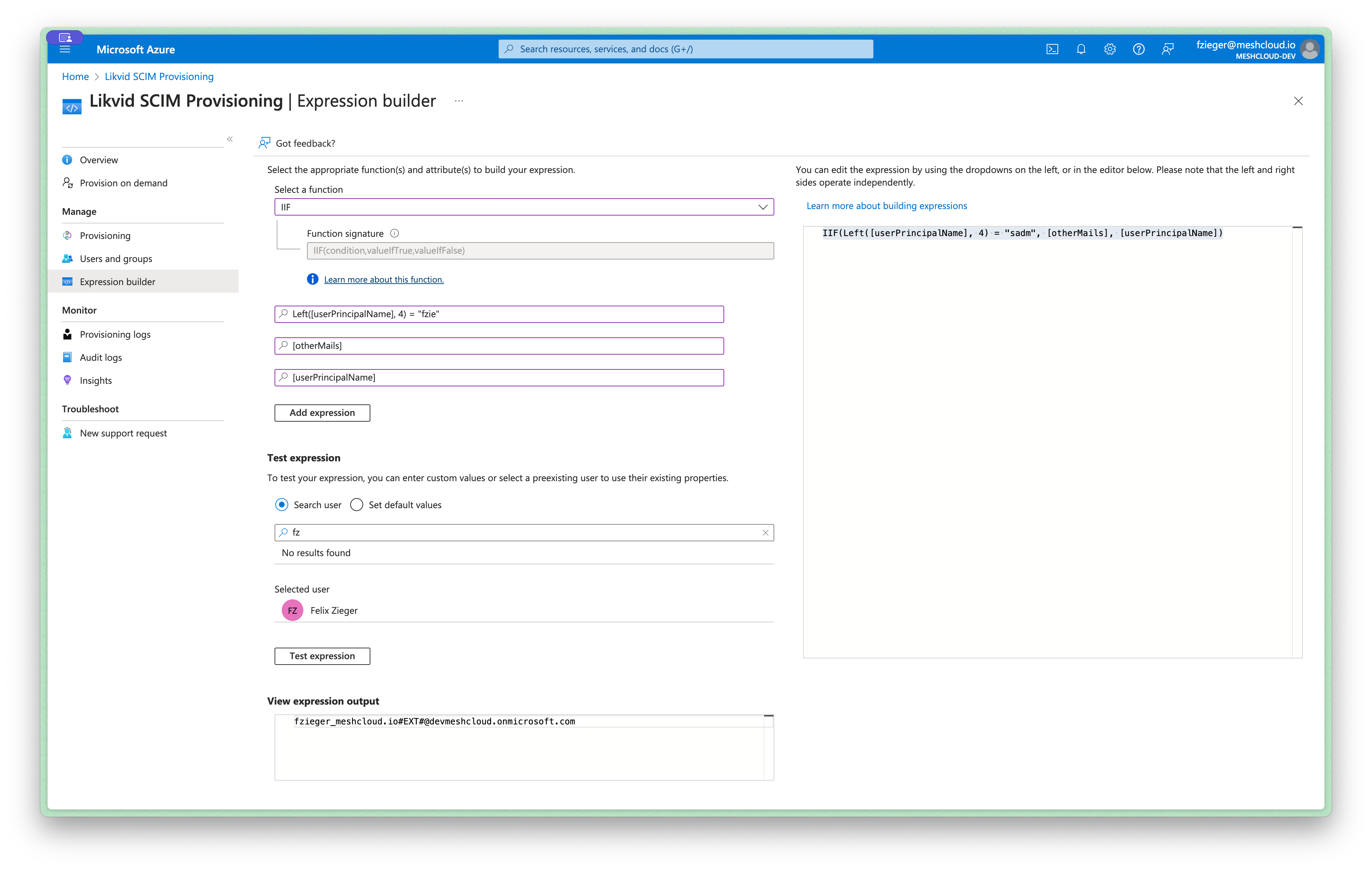
In this example, the expression is IIF(Left([userPrincipalName], 4) = "sadm", [otherMails], [userPrincipalName]).
When a user's userPrincipalName begins with sadm, the otherMails attribute is retrieved. If it does not begin with sadm, then the userPrincipalName itself is returned.
After finalizing the expression, proceed to open the user mapping settings.
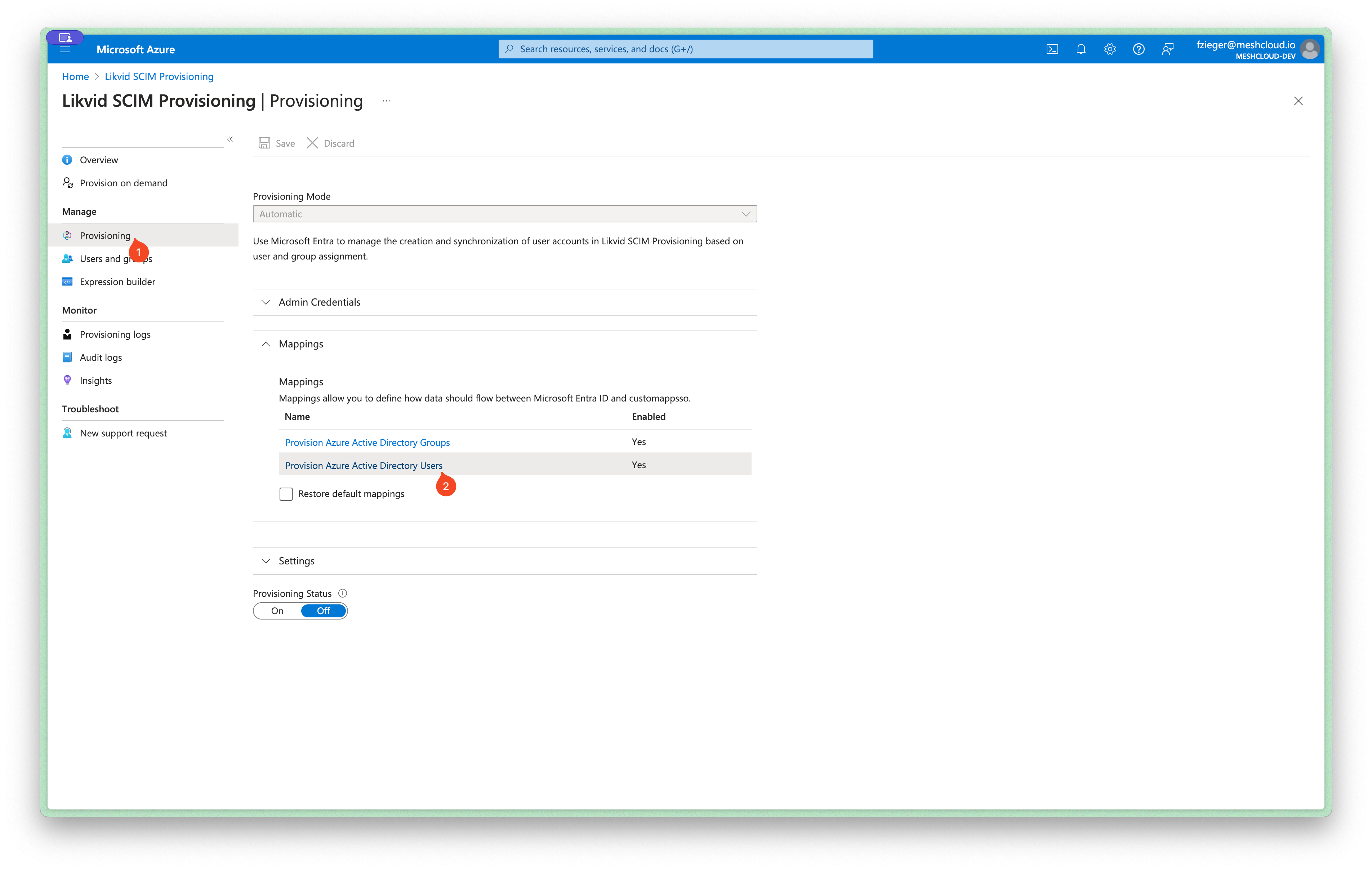
Within the user mappings table, edit the attribute you want to modify.
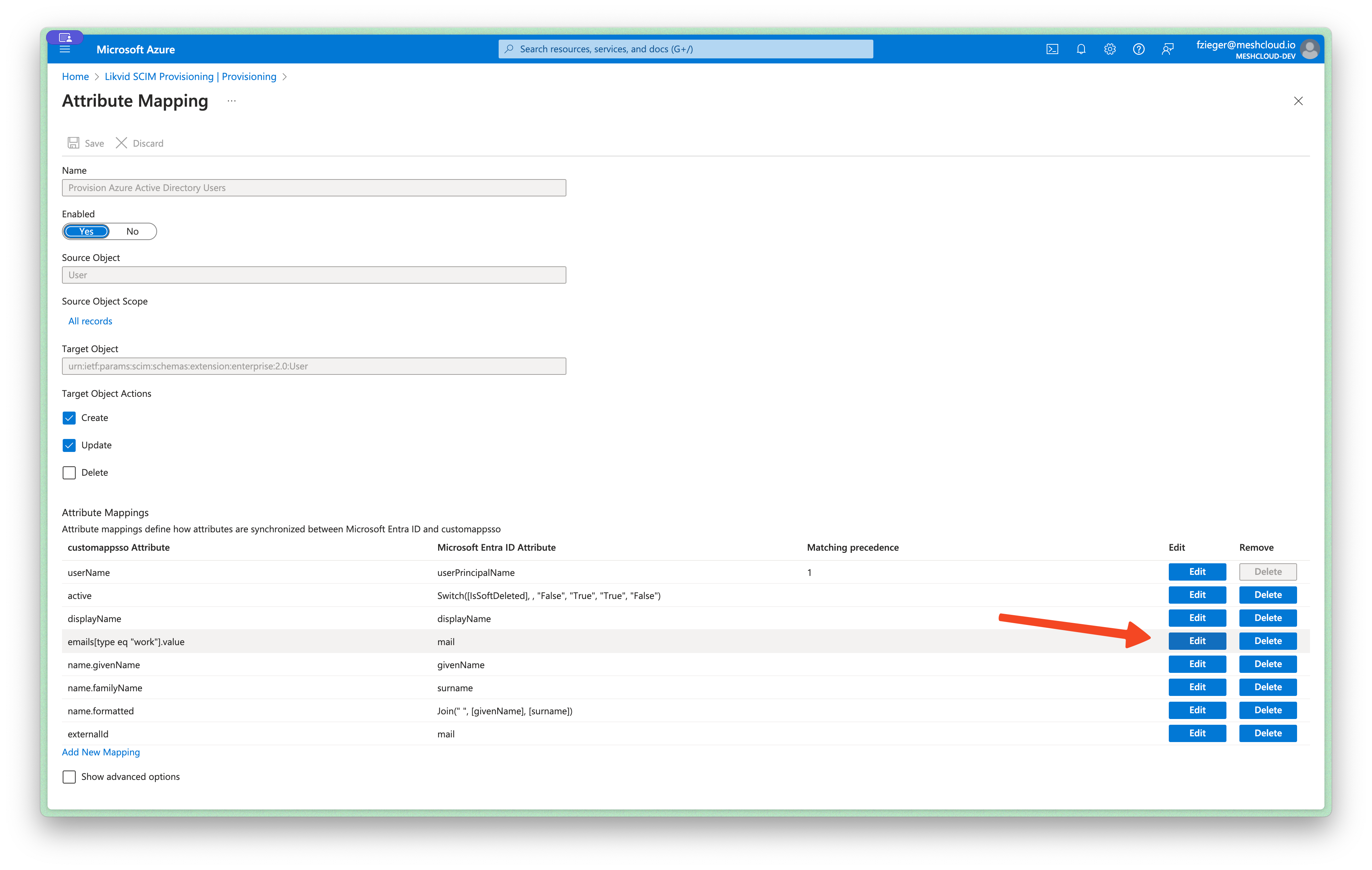
Choose Mpaping type Expression and insert the expression you have built earlier.
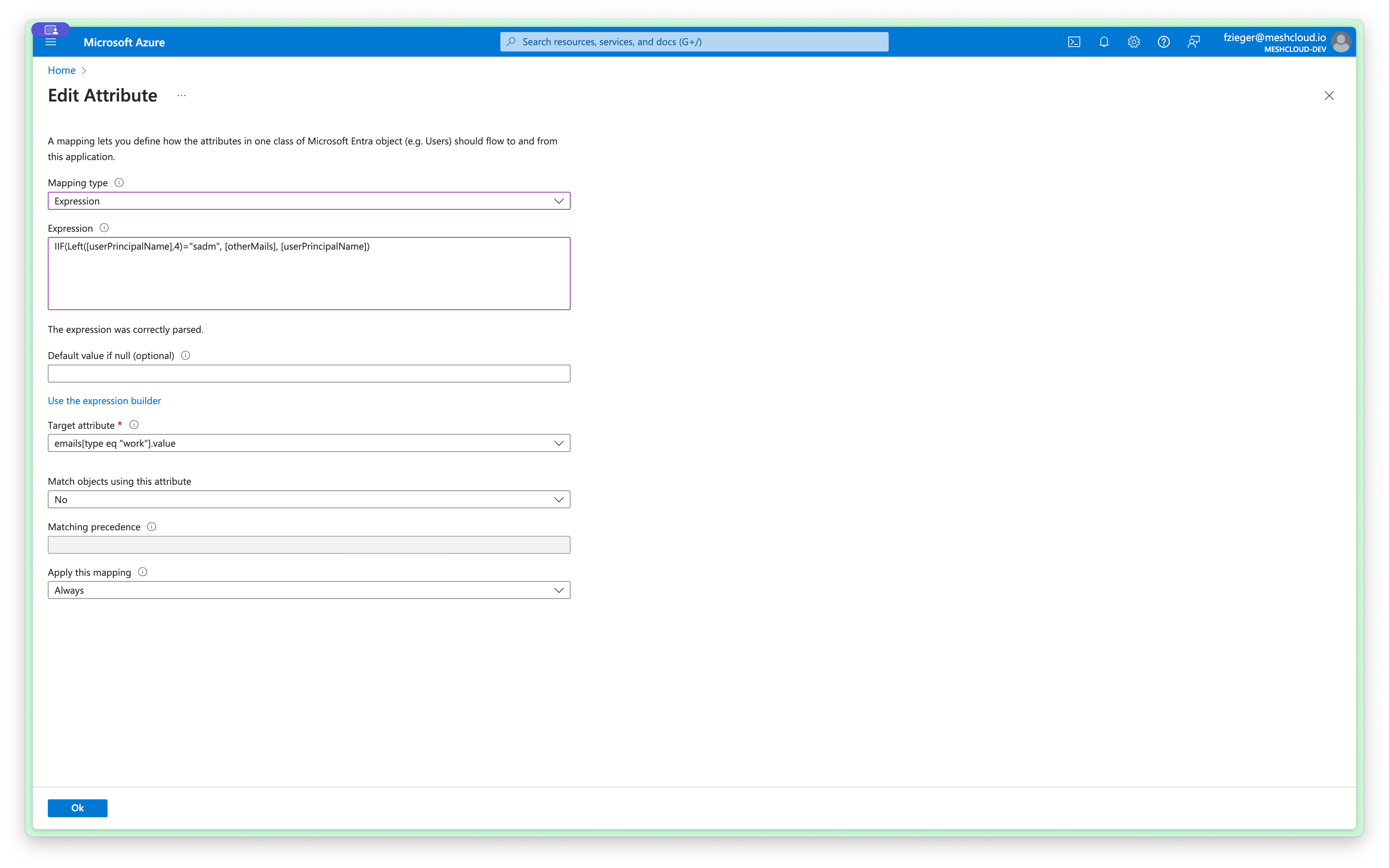
The synchronisation will now use the expression to map values from Entra ID to meshStack users.
User Lifecycle with Microsoft Entra ID and SCIM
The following section describes how users are created and removed from meshStack when you have Azure Active Directory (AAD) configured as described above.
Creation
Entra ID sends a request to create a user via SCIM if that user is in the provisioning scope of the Enterprise Application.
Deactivation
SCIM deactivation requests are sent, for example, in the following cases:
- A user has moved out of the provisioning scope.
- A user was explicitly disabled in Entra ID.
- A user was removed in AAD, but not permanently deleted yet: If the user is still visible in the "Deleted users" section in AAD, then the user is deactivated, but not deleted.
Deactivating a user via SCIM has the following consequences in meshStack:
- The user will have their access rights revoked from all platforms.
- The user will be unable to log in to meshPanel. This is also the case when federated authentication is used with an IdP other than Microsoft Entra ID. For example, if Microsoft Entra ID is used to synchronize users to meshStack, but Google SSO is used for authentication, users are unable to login if Entra ID deactivated them via SCIM, regardless of their activation status in Google.
User deactivation is reversible: If meshStack subsequently receives an SCIM request to activate this user, then the user will regain their previous access rights on all platforms as well as the possibility to log in to meshPanel.
Deletion
SCIM deletion requests are sent, for example, in the following cases:
- The user was permanently deleted in Entra ID.
- The user was previously deleted in Entra ID, and has now automatically been permanently deleted in Entra ID after a given period (usually 30 days) has passed.
Attention: A previous version of this guide has explicitly demanded to configure AAD such that user deletion via SCIM is disabled, because previous versions of meshStack did not support deletion. With the current version of meshStack, deletion is supported. If you have previously disabled user deletion and now want to enable it, please proceed as follows:
In the Azure portal, visit the service "Azure Active Directory" and the section "Enterprise Application". Then, navigate to "Provisioning" → "Edit attribute mappings" to see the user mapping. Below "Target Object Actions", three checkboxes are displayed: "Create", "Update" and "Delete". Ensure that all three checkboxes are checked.
Deleting a user via SCIM has the following consequences in meshStack: The user will be irrevocably deleted and only the bare minimum of information required for GDPR compliance is retained. After deletion, it is possible to create a new user with the same username and email as the previously deleted user, but the deleted user cannot be restored.